Harmful Mold?
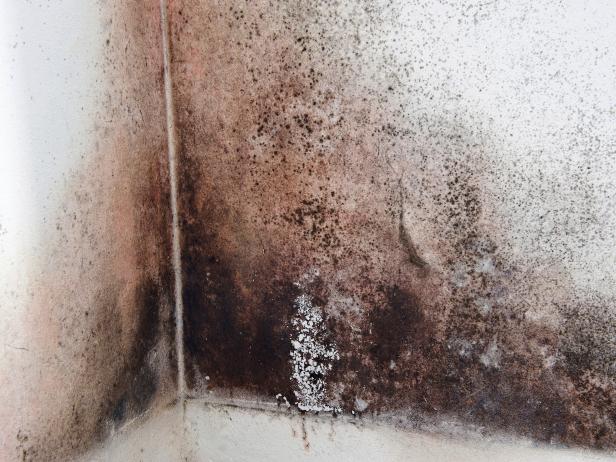
Mold spores are everywhere in our environment. With the presence of moisture and oxygen mold spores attack and attempt to decompose any organic substance. Many materials used in the construction of your home are subject to attack by mold; Insulation, carpet, wood, drywall paper. Even concrete can be the target of natural mold decomposition. Many types of mold left undiscovered or unaddressed moisture problems turn to mold problems. Mold problems can cause hazardous health conditions in your home as well as structural damage to your home. It’s a particular problem in the Pacific Northwest.
The key to mold control is moisture control and our proprietary EWA system (Extreme Water Abandonment – with Permanent Mold Control) provides a permanent and complete water and mold control solution, with a Lifetime Guarantee. WET BASEMENT SERVICES is a state licensed company that offers mold and moisture control, basement waterproofing and mold removal services to the greater Seattle area.




Mold Control: Essential Methods for a Healthier Home
Understanding Mold Growth
Key Methods for Controlling Mold
1. Manage Moisture and Humidity
Mold control starts with moisture control. Keeping indoor humidity below 50% prevents mold spores from thriving. This can be achieved by:
- Using a dehumidifier, especially in basements or high-humidity areas
- Ventilating showers, cooking areas, and other spaces that generate moisture
- Repairing any plumbing leaks or roof leaks promptly
2. Ventilation Improvements
Proper ventilation is essential in preventing mold. Bathrooms, kitchens, and laundry rooms should be equipped with exhaust fans that vent moisture outdoors. Opening windows regularly can also improve air circulation, reducing trapped humidity.
3. Fix Leaks and Address Water Intrusion
Water leaks are one of the most common causes of mold growth. Regularly inspect areas under sinks, around showers, and near roofs for any signs of leaks. Fixing cracks in foundations and walls can also help to prevent water from seeping indoors.
4. Install Waterproofing Solutions
For basements and crawl spaces prone to dampness, waterproofing solutions can make a significant difference. Sump pumps, drainage systems, and vapor barriers help to keep these areas dry, preventing mold from taking hold.
5. Clean and Dry Damp Surfaces Promptly
After any flooding or water spills, it’s crucial to dry the area thoroughly within 24 to 48 hours to prevent mold from setting in. Use fans, towels, and, if necessary, a professional drying service to handle extensive water issues.
6. Use Mold-Resistant Materials
When renovating or building, consider using mold-resistant drywall, insulation, and paint, especially in high-moisture areas. These materials contain properties that inhibit mold growth and are especially useful in bathrooms, kitchens, and basements.
7. Regular Cleaning and Maintenance
Regular cleaning with mold-inhibiting products helps prevent mold growth in frequently used areas. Clean HVAC systems, as mold spores can spread through ventilation ducts, and maintain gutters to avoid water pooling near foundations.
